Example
To make a brouter (the router that routes routable (IP in our case) protocols and bridges unroutable protocols), make a rule that drops IP, ARP and RARP traffic (these protocols should be disabled in bridge firewall, not in forwarded protocols as in the other case the router will not be able to receive IP packets itself, and thus will not be able to provide routing).To make bridge drop IP, ARP ad RARP packets:
[admin@MikroTik] interface bridge firewall> add mac-protocol=2048 action=drop
[admin@MikroTik] interface bridge firewall> add mac-protocol=2054 action=drop
[admin@MikroTik] interface bridge firewall> add mac-protocol=32821 action=drop
[admin@MikroTik] interface bridge firewall> print
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid
0 mac-src-address=00:00:00:00:00:00 in-interface=all
mac-dst-address=00:00:00:00:00:00 out-interface=all mac-protocol=2048
src-address=0.0.0.0/0 dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 protocol=all action=drop
1 mac-src-address=00:00:00:00:00:00 in-interface=all
mac-dst-address=00:00:00:00:00:00 out-interface=all mac-protocol=2054
src-address=0.0.0.0/0 dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 protocol=all action=drop
2 mac-src-address=00:00:00:00:00:00 in-interface=all
mac-dst-address=00:00:00:00:00:00 out-interface=all mac-protocol=32821
src-address=0.0.0.0/0 dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 protocol=all action=drop
[admin@MikroTik] interface bridge firewall>
Application Example
Assume we want to enable bridging between two Ethernet LAN segments and have the MikroTik router be the default gateway for them:
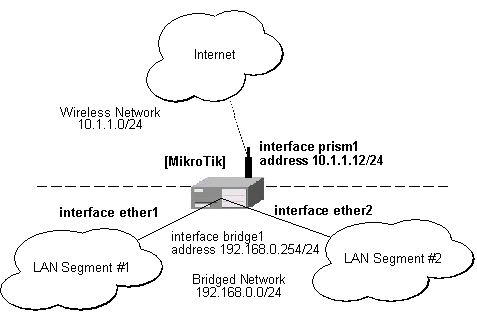
When configuring the MikroTik router for bridging you should do the following:
- Add bridge interface
- Configure the bridge interface
- Enable the bridge interface
- Assign an IP address to the bridge interface, if needed
Note that there should be no IP addresses on the bridged interfaces. Moreover, IP address on the bridge interface itself is not required for the bridging to work.
When configuring the bridge settings, each protocol that should be forwarded should be added to the forward-protocols list. The other protocol includes all protocols not listed before (as VLAN).
[admin@MikroTik] interface bridge> add forward-protocols=ip,arp,other
[admin@MikroTik] interface bridge> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 X name="bridge1" mtu=1500 arp=enabled mac-address=00:00:00:00:00:00
forward-protocols=ip,arp,other priority=1
[admin@MikroTik] interface bridge>
The priority argument is used by the Spanning Tree Protocol to determine,
which port remains enabled if two ports form a loop.
Next, each interface that should be included in the bridging port table:
[admin@MikroTik] interface bridge port> print Flags: X - disabled # INTERFACE BRIDGE 0 ether1 none 1 ether2 none 2 ether3 none 3 prism1 none [admin@MikroTik] interface bridge port> set "0,1" bridge=bridge1 [admin@MikroTik] interface bridge port> print Flags: X - disabled # INTERFACE BRIDGE 0 ether1 bridge1 1 ether2 bridge1 2 ether3 none 3 prism1 none [admin@MikroTik] interface bridge port>
After setting some interface for bridging, the bridge interface should be enabled in order to start using it:
[admin@MikroTik] interface bridge> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 X name="bridge1" mtu=1500 arp=enabled mac-address=00:50:08:00:00:F5
forward-protocols=ip,arp,other priority=1
[admin@MikroTik] interface bridge> enable 0
[admin@MikroTik] interface bridge> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 R name="bridge1" mtu=1500 arp=enabled mac-address=00:50:08:00:00:F5
forward-protocols=ip,arp,other priority=1
[admin@MikroTik] interface bridge>
If you want to access the router through unnumbered bridged interfaces, it is required to add an IP address to the bridge interface:
[admin@MikroTik] ip address> add address=192.168.0.254/24 interface=bridge1 [admin@MikroTik] ip address> add address=10.1.1.12/24 interface=prism1 [admin@MikroTik] ip address> print Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic # ADDRESS NETWORK BROADCAST INTERFACE 0 192.168.0.254/24 192.168.0.0 192.168.0.255 bridge1 1 10.1.1.12/24 10.1.1.0 10.1.1.255 prism1 [admin@MikroTik] ip address>
Note!Assigning an IP address to bridged interfaces ether1 or ether2 has no sense. Thus, when you assign an interface to a bridge, you should move its IP address to the bridge interface at the same time!
Hosts on LAN segments #1 and #2 should use IP addresses from the same network 192.168.0.0/24 and have the default gateway set to 192.168.0.254 (MikroTik router).
Additional Bridge Firewall Resources
Links for Bridge Firewall documentation:
http://users.pandora.be/bart.de.schuymer/ebtables/br_fw_ia/br_fw_ia.html
Troubleshooting
- After I configure the bridge, there is no ping response from hosts on bridged networks.
It may take up to 20...30s for bridge to learn addresses and start responding. - When I do a Bridge between the Ethernet and Wireless Interface
I lost the network connection to the router via Ethernet
When network interface is assigned to a bridge, its ip address should be set on the bridge interface as well. Leaving IP address on a bridged interface has no sense. - I have added a bridge interface, but no IP traffic is passed.
You should include 'arp' in forwarded protocols list, e.g., 'forward-protocols=ip,arp,other'.
© Copyright 1999-2002, MikroTik