MikroTik RouterOS has following types of addresses:
[MikroTik] ip address>
IP addresses are given to router to access it remotely and to specify it as a
gateway for other hosts/routers.
print Show IP addresses
get get value of item's property
find Find addresses
set Change IP address properties
add Add IP address
remove Remove IP address
enable Enable IP address
disable Disable IP address
comment Set comment for IP address
export Export list of IP addresses
[MikroTik] ip address>
Use the /ip address add command to add an IP address to an interface. In most cases, it is enough to specify the address, the netmask, and the interface arguments. The network prefix and the broadcast address are calculated automatically, for example:
[MikroTik] ip address> add address=192.168.0.254/24 interface=Local [MikroTik] ip address> print Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic # ADDRESS NETWORK BROADCAST INTERFACE 0 192.168.0.254/24 192.168.0.0 192.168.0.255 Local [MikroTik] ip address>
Description of the arguments:
number - number assigned to the item in the list
flag - shows the status of the item
address - local IP address, can be in the form address/mask, where mask is number of bits in the subnet mask.
netmask - network mask to be used with the network prefix. Must be in the decimal form xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
network - (optional) network prefix to be used with the address. It shows what network can be reached through the interface with the given IP address. If not specified, will be calculated from local address and network mask. For point-to-point links should be the address of the remote end.
broadcast - (optional) broadcast address to be used with the address. If not specified, will be calculated from local address and network mask.
interface - name of the interface the address will be used with
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
Address Resolution Protocol is used to map IP address to MAC layer address.
Router has a table of currently used ARP entries. Normally table is built
dynamically, but to increase network security, static entries can be added.
The ARP management can be accessed under the /ip arp submenu:
[MikroTik] ip arp> ?
add Add static ARP entry
comment Set comment for ARP entry
disable Disable static ARP entry
enable Enable static ARP entry
export Export list of ARP entries
find Find ARP entries
get Get value of item's property
print Show ARP entries
remove Remove ARP entry
set Change ARP entry properties
[MikroTik] ip arp>
To view the list of arp entries, use the /ip arp print command:
[MikroTik] ip arp> print Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic # ADDRESS MAC-ADDRESS INTERFACE 0 D 10.1.1.254 00:80:C8:C9:B0:45 Public 1 D 10.5.8.214 08:00:46:04:33:17 Local 2 D 10.5.9.202 00:00:E8:69:65:5F sales 3 D 10.5.9.204 00:00:E8:69:69:9F sales 4 D 10.5.8.204 00:60:52:0B:B4:80 Local [MikroTik] ip arp>
If static arp entries are used for network security on an interface, you should disable arp on the relevant interface under the /interfaces menu and add the static arp entries:
[MikroTik] ip arp> /interface ethernet set Local arp=disabled [MikroTik] ip arp> add address=10.5.8.214 mac-address=08:00:46:04:33:17 interface=Local [MikroTik] ip arp> print Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic # ADDRESS MAC-ADDRESS INTERFACE 0 D 10.1.1.254 00:80:C8:C9:B0:45 Public 1 10.5.8.214 08:00:46:04:33:17 Local 2 D 10.5.9.202 00:00:E8:69:65:5F sales 3 D 10.5.9.204 00:00:E8:69:69:9F sales [MikroTik] ip arp>
Since the ARP requests from the clients are not answered by the router, if the arp feature is turned off on the interface, static arp entry should be added to the clients as well. For example, the router's IP and MAC addresses should be added to the windows workstations using the 'arp' command, for example:
C:\> arp -s 10.5.8.254 00-aa-00-62-c6-09
See the relevant documentation on how to manage static arp entries on your system.
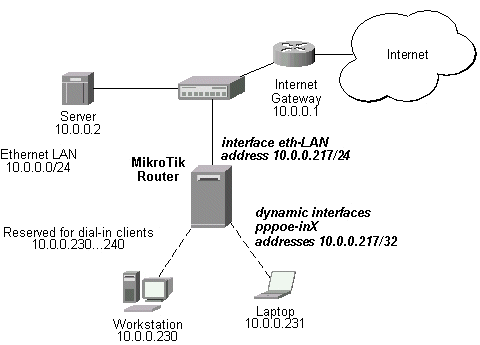
All physical interfaces, like Ethernet, Prism, Aironet (PC), WaveLAN, etc., can be set for using the Address Resolution Protocol or not. By default, the arp feature is 'enabled'. However, it can be changed to 'proxy-arp'. The Proxy-ARP feature means that the router will be listening to arp requests received at the relevant interface and respond to them with it's own MAC address, if the requests matches any other IP address of the router. For example, you can assign IP addresses to dial-in (ppp, pppoe, pptp) clients from the same address space as used on the connected LAN, of you enable the 'proxy-arp' on the LAN interface. Let us consider the following setup:

The MikroTik router setup is as follows:
[MikroTik] > interface ethernet print
Flags: X - disabled
# NAME MTU MAC-ADDRESS ARP
0 eth-LAN 1500 00:E0:C5:BC:12:1C proxy-arp
[MikroTik] > interface print
Flags: X - disabled, D - dynamic
# NAME TYPE MTU
0 eth-LAN ether 1500
1 prism1 prism 1500
2 D pppoe-in25 pppoe-in
3 D pppoe-in26 pppoe-in
[MikroTik] > ip address print
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic
# ADDRESS NETWORK BROADCAST INTERFACE
0 10.0.0.217/24 10.0.0.0 10.0.0.255 eth-LAN
1 D 10.0.0.217/32 10.0.0.230 0.0.0.0 pppoe-in25
2 D 10.0.0.217/32 10.0.0.231 0.0.0.0 pppoe-in26
[MikroTik] > ip route print
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic, J - rejected,
C - connect, S - static, R - rip, O - ospf, B - bgp
# DST-ADDRESS G GATEWAY DISTANCE INTERFACE
0 S 0.0.0.0/0 r 10.0.0.1 1 eth-LAN
1 DC 10.0.0.0/24 r 0.0.0.0 0 eth-LAN
2 DC 10.0.0.230/32 r 0.0.0.0 0 pppoe-in25
3 DC 10.0.0.231/32 r 0.0.0.0 0 pppoe-in26
[MikroTik] >
The unnumbered interfaces can be used on serial point-to-point links, e.g., MOXA C101, Cyclades interfaces. A private address should be put on the interface with the "network" being the same as an address on the router on the other side of the p2p link (there may be no IP on that interface, but there is an ip for that router). For example:
[MikroTik] ip address>
add address=10.0.0.214/32 network=192.168.0.1 interface=pppsync
[MikroTik] ip address> print
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic
# ADDRESS NETWORK BROADCAST INTERFACE
0 10.0.0.214/32 192.168.0.1 192.168.0.1 pppsync
[MikroTik] ip address>
[MikroTik] ip address> .. route print detail
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic, J - rejected,
C - connect, S - static, R - rip, O - ospf, B - bgp
0 S dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 preferred-source=0.0.0.0 gateway=192.168.0.1
gateway-state=reachable distance=1 interface=pppsync
1 DC dst-address=192.168.0.1/32 preferred-source=10.0.0.214
gateway=0.0.0.0 gateway-state=reachable distance=0 interface=pppsync
[MikroTik] ip address>
Here, you can see, that a dynamic connected route has been automatically added to the routes list. If you want the default gateway be the other router of the p2p link, just add a static route for it. It is shown as #0 in the example above.