Document revision 1.6 (19-Aug-2003)
This document applies to the MikroTik RouterOS V2.7
| DB25f | Signal | Direction | V.35m |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | RTS | OUT | C |
| 5 | CTS | IN | D |
| 6 | DSR | IN | E |
| 7 | GND | - | B |
| 8 | DCD | IN | F |
| 10 | TxDB | OUT | S |
| 11 | TxDA | OUT | P |
| 12 | RxDB | IN | T |
| 13 | RxDA | IN | R |
| 14 | TxCB | IN | AA |
| 16 | TxCA | IN | Y |
| 20 | DTR | OUT | H |
| 22 | RxCB | IN | X |
| 23 | RxCA | IN | V |
| short 9 and 25 pin | |||
The MikroTik driver for the MOXA C101 Synchronous adapter allows you to unplug the V.35 cable from one modem and plug it into another modem with a different clock speed, and you do not need to restart the interface or router.
[admin@MikroTik] interface> moxa-c101
[admin@MikroTik] interface moxa-c101> print
Flags: X - disabled, R - running
0 R name="moxa-c101-1" mtu=1500 line-protocol=sync-ppp clock-rate=64000
clock-source=external frame-relay-lmi-type=ansi frame-relay-dce=no
cisco-hdlc-keepalive-interval=10s ignore-dcd=no
[admin@MikroTik] interface moxa-c101>
You can monitor the status of the synchronous interface:
[admin@MikroTik] interface moxa-c101> monitor 0
dtr: yes
rts: yes
cts: no
dsr: no
dcd: no
[admin@MikroTik] interface moxa-c101>
Connect a communication device, e.g., a baseband modem, to the V.35 port and turn it on.
If the link is working properly the status of the interface is:
[admin@MikroTik] interface moxa-c101> monitor 0
dtr: yes
rts: yes
cts: yes
dsr: yes
dcd: yes
[admin@MikroTik] interface moxa-c101>
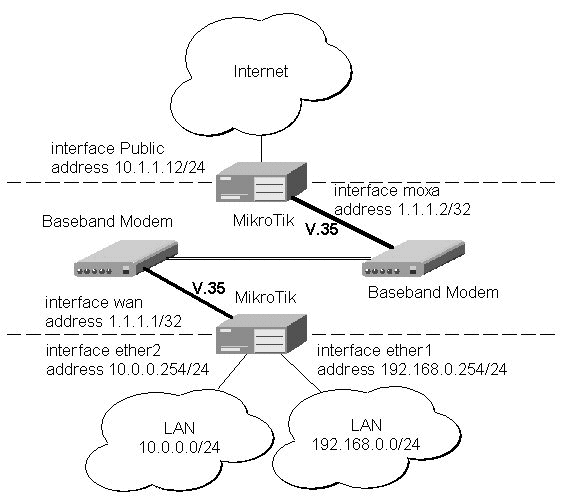
Let us consider the following network setup with two MikroTik Routers connected to a leased line with baseband modems:

The driver for MOXA C101 card should be loaded and the interface should be enabled according to the instructions given above. The IP addresses assigned to the synchronous interface should be as follows:
[admin@MikroTik] ip address> add address 1.1.1.1/32 interface wan \ \... network 1.1.1.2 broadcast 255.255.255.255 [admin@MikroTik] ip address> print Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic # ADDRESS NETWORK BROADCAST INTERFACE 0 10.0.0.254/24 10.0.0.254 10.0.0.255 ether2 1 192.168.0.254/24 192.168.0.254 192.168.0.255 ether1 2 1.1.1.1/32 1.1.1.2 255.255.255.255 wan [admin@MikroTik] ip address> /ping 1.1.1.2 1.1.1.2 64 byte pong: ttl=255 time=31 ms 1.1.1.2 64 byte pong: ttl=255 time=26 ms 1.1.1.2 64 byte pong: ttl=255 time=26 ms 3 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 26/27.6/31 ms [admin@MikroTik] ip address>The default route should be set to the gateway router 1.1.1.2:
[admin@MikroTik] ip route> add gateway 1.1.1.2
[admin@MikroTik] ip route> print
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic, J - rejected,
C - connect, S - static, R - rip, O - ospf, B - bgp
# DST-ADDRESS G GATEWAY DISTANCE INTERFACE
0 S 0.0.0.0/0 r 1.1.1.2 1 wan
1 DC 10.0.0.0/24 r 10.0.0.254 1 ether2
2 DC 192.168.0.0/24 r 192.168.0.254 0 ether1
3 DC 1.1.1.2/32 r 0.0.0.0 0 wan
[admin@MikroTik] ip route>
The configuration of the Mikrotik router at the other end is similar:
[admin@MikroTik] ip address> add address 1.1.1.2/32 interface moxa \ \... network 1.1.1.1 broadcast 255.255.255.255 [admin@MikroTik] ip address> print Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic # ADDRESS NETWORK BROADCAST INTERFACE 0 10.1.1.12/24 10.1.1.12 10.1.1.255 Public 1 1.1.1.2/32 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 moxa [admin@MikroTik] ip address> /ping 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 64 byte pong: ttl=255 time=31 ms 1.1.1.1 64 byte pong: ttl=255 time=26 ms 1.1.1.1 64 byte pong: ttl=255 time=26 ms 3 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 26/27.6/31 ms [admin@MikroTik] ip address>
Let us consider the following network setup with MikroTik Router connected to a leased line with baseband modems and a CISCO router at the other end:
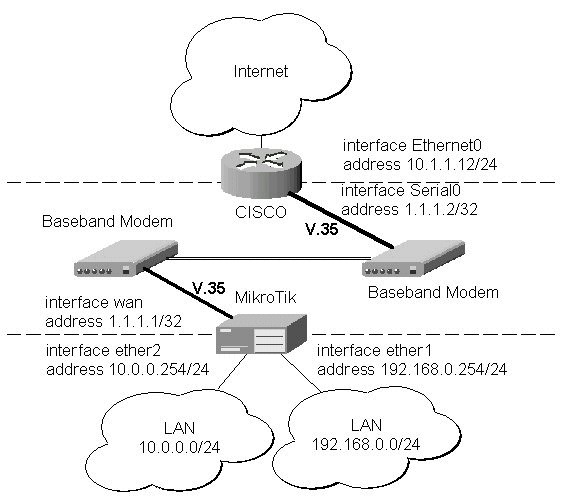
The driver for MOXA C101 card should be loaded and the interface should be enabled according to the instructions given above. The IP addresses assigned to the synchronous interface should be as follows:
[admin@MikroTik] ip address> add address 1.1.1.1/32 interface wan \ \... network 1.1.1.2 broadcast 255.255.255.255 [admin@MikroTik] ip address> print Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic # ADDRESS NETWORK BROADCAST INTERFACE 0 10.0.0.254/24 10.0.0.254 10.0.0.255 ether2 1 192.168.0.254/24 192.168.0.254 192.168.0.255 ether1 2 1.1.1.1/32 1.1.1.2 255.255.255.255 wan [admin@MikroTik] ip address> /ping 1.1.1.2 1.1.1.2 64 byte pong: ttl=255 time=31 ms 1.1.1.2 64 byte pong: ttl=255 time=26 ms 1.1.1.2 64 byte pong: ttl=255 time=26 ms 3 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 26/27.6/31 ms [admin@MikroTik] ip address>The default route should be set to the gateway router 1.1.1.2:
[admin@MikroTik] ip route> add gateway 1.1.1.2
[admin@MikroTik] ip route> print
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic, J - rejected,
C - connect, S - static, R - rip, O - ospf, B - bgp
# DST-ADDRESS G GATEWAY DISTANCE INTERFACE
0 S 0.0.0.0/0 r 1.1.1.2 1 wan
1 DC 10.0.0.0/24 r 10.0.0.254 0 ether2
2 DC 192.168.0.0/24 r 192.168.0.254 0 ether1
3 DC 1.1.1.2/32 r 1.1.1.1 0 wan
[admin@MikroTik] ip route>
The configuration of the CISCO router at the other end (part of the configuration) is:
CISCO#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration: ... ! interface Ethernet0 description connected to EthernetLAN ip address 10.1.1.12 255.255.255.0 ! interface Serial0 description connected to MikroTik ip address 1.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 serial restart-delay 1 ! ip classless ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.254 ! ... end CISCO#Send ping packets to the MikroTik router:
CISCO#ping 1.1.1.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 1.1.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 28/32/40 ms CISCO#